
Structural Design
The beauty of a structure lies in its simplicity and functionality.
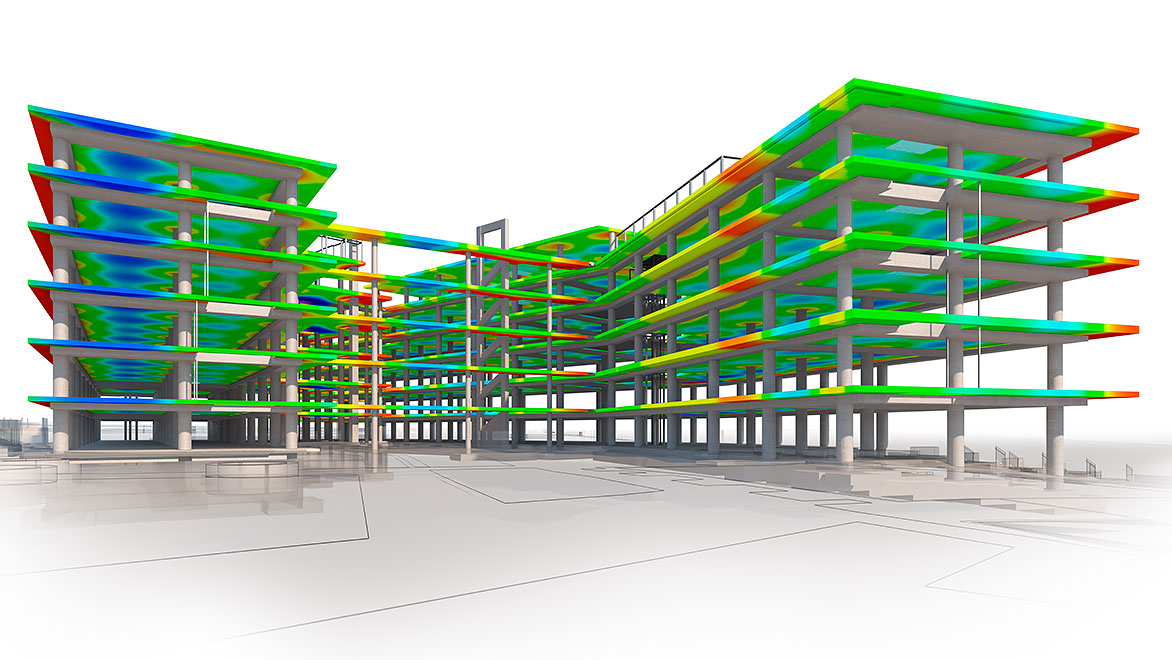
Foundation Selection
- Choose the appropriate foundation type (shallow or deep) based on soil bearing capacity (SBC).
- Use raft or pile foundations for weak or expansive soils and strip or isolated footings for stable soils.
- Ensure proper compaction and reinforcement to prevent settlement and structural failure.
Load-Bearing Capacity & Structural Integrity
- Design columns, beams, and slabs to distribute loads effectively based on soil strength.
- Modify structural elements if uneven settlement or weak soil zones are identified.
- Ensure proper reinforcement in seismic-prone or flood-prone areas.
Waterproofing & Drainage Considerations
- Implement moisture barriers and waterproofing solutions in areas with high water tables.
- Design effective drainage systems to prevent water retention near foundations.
- Use soil stabilization techniques like sand filling, gravel layering, or chemical treatment if needed.
Structural Modifications for Soil Conditions
- Adjust building height, load distribution, and material selection based on soil conditions.
- Use expansion joints and flexible materials in regions with shrinkswell soil behavior.
- Ensure compliance with seismic design codes for earthquakeprone areas.
BIDDING & NEGOTIATION
- Assigning a contractor and finalize the construction contract.
- Issuing construction documents to contractors, evaluate bids, and negotiate terms.
- A signed contract with a chosen contractor, ready to begin construction.
CONSTRUCTION & ADMINISTRATION
- Oversee construction to ensure design intent is met.
- Site visits, reviewing submittals, addressing RFIs (Requests for Information), and managing changes.
- A completed project delivered according to design, budget, and schedule, with a final walkthrough and punch list.

